| We have two databases in the same SQL server instance. Both of the databases are copy of the production database, so both contains same tables. We added some records in Test Database’s some tables to update some features. We have added data in many tables of test database. Now we need to also update Production DB with the updated data. To update Production Database, we need to make sure in which tables we have updated data and then we will check and update production database accordingly. We have many numbers of tables, and we have updated many tables, so its not possible for us to check it manually. So, we need to make query to compare rows of each table with the another database tables, to find out which tables has different rows then the original database. Solution: As I need to solve this problem, I write a query which will give me Rows of each table in one Database. As I need to compare it with another database I write the following query to come out with the solution. Example: I have two databases. Database A and Database B. I need to make a report, which will give me details of each table and rows. I made this Stored Procedure in Database A. CREATE PROC CompareRowsBetweenDatabas This will give me results as I need. Let me know if it helps you. |
Learn SQL and database management at SQLYoga for articles, tutorials, and tips to improve your skills and streamline data operations. Join our community!
April 26, 2009
SQL SERVER - Query to compare number of Rows between different Databases
 18+ years of Hands-on Experience
MICROSOFT CERTIFIED PROFESSIONAL (Microsoft SQL Server)
Proficient in .NET C#
Hands on working experience on MS SQL, DBA, Performance Tuning, Power BI, SSIS, and SSRS
18+ years of Hands-on Experience
MICROSOFT CERTIFIED PROFESSIONAL (Microsoft SQL Server)
Proficient in .NET C#
Hands on working experience on MS SQL, DBA, Performance Tuning, Power BI, SSIS, and SSRS
April 20, 2009
SQL SERVER: Get Result ORDER BY Time regardless Date on SQL DateTime column
Usually we save Time with Dates in DATETIME column.
Today, I came across situation, where I need to sort my result set by Time, regardless the Date.
I have some sample data like this:
DECLARE @Data TABLE(dt DATETIME)
INSERT INTO @Data(dt)
SELECT '2008-12-05 04:00:00.000'
UNION ALL
SELECT '2008-12-10 10:00:00.000'
UNION ALL
SELECT '2009-03-01 08:00:00.000'
UNION ALL
SELECT '2009-03-02 07:15:00.000'
UNION ALL
SELECT '2009-03-10 08:50:00.000'
UNION ALL
SELECT '2008-12-31 23:00:00.000'
UNION ALL
SELECT '2009-05-01 21:10:00.000'
SELECT * FROM @Data
I found very quick solution for this. You can create query as follows:
SELECT *
FROM @Data
ORDER BY Convert(VARCHAR, dt,108)
Let me know if it helps you in any way.
 18+ years of Hands-on Experience
MICROSOFT CERTIFIED PROFESSIONAL (Microsoft SQL Server)
Proficient in .NET C#
Hands on working experience on MS SQL, DBA, Performance Tuning, Power BI, SSIS, and SSRS
18+ years of Hands-on Experience
MICROSOFT CERTIFIED PROFESSIONAL (Microsoft SQL Server)
Proficient in .NET C#
Hands on working experience on MS SQL, DBA, Performance Tuning, Power BI, SSIS, and SSRS
April 15, 2009
SQL SERVER: Difference between OpenQuery and OpenRowSet
Today, one developer asked me what is the difference between OpenQuery and OpenRowSet.
Let me share this thing with all of you.
Syntax for both the command:
OPENQUERY ( linked_server ,'query' )
OPENROWSET
( 'provider_name' , 'datasource' ; 'user_id' ; 'password'
, { [ catalog. ] [ schema. ] object | 'query' }
)
Difference is:
OpenQuery uses a predefined linked server,
While OpenRowSet has to specify all the connection options. So with OpenRowSet you can query to your remote SQL server from local.
Else it's the same.
Let me know if it helps you in any way.
 18+ years of Hands-on Experience
MICROSOFT CERTIFIED PROFESSIONAL (Microsoft SQL Server)
Proficient in .NET C#
Hands on working experience on MS SQL, DBA, Performance Tuning, Power BI, SSIS, and SSRS
18+ years of Hands-on Experience
MICROSOFT CERTIFIED PROFESSIONAL (Microsoft SQL Server)
Proficient in .NET C#
Hands on working experience on MS SQL, DBA, Performance Tuning, Power BI, SSIS, and SSRS
April 14, 2009
SQL SERVER: SQL Query To Find Most used Tables
| We have very large database and today we want to search the tables which are used mostly. Means tables which are used in Procedures, Constraints, Views, Triggers etc. I know this is very strange requirement, but we need to do this. So, I tried to make an query which will help me to find out the top most tables used in other objects as I mentioned Let me share that sp with all of you: SELECT TableName, COUNT(*) So, I made my life easy, by using this. I can get the list if Tables which are used most. Let me know if it helps you in any way. |
 18+ years of Hands-on Experience
MICROSOFT CERTIFIED PROFESSIONAL (Microsoft SQL Server)
Proficient in .NET C#
Hands on working experience on MS SQL, DBA, Performance Tuning, Power BI, SSIS, and SSRS
18+ years of Hands-on Experience
MICROSOFT CERTIFIED PROFESSIONAL (Microsoft SQL Server)
Proficient in .NET C#
Hands on working experience on MS SQL, DBA, Performance Tuning, Power BI, SSIS, and SSRS
April 2, 2009
SQL SEVER: How to make an Entry in Event Viewer using SQL SERVER
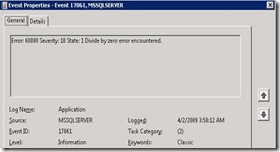
| Today I came across the situation where I need to following scenario. I need to make entry in Event Viewer when there is an error in Stored Procedure. I wondered to do this, but finally I come up with the solution. SQL is much powerful. SQL provides us to make an entry in Event Viewer by two ways: 1. using XP_LogEvent 2. By Raiserror WITH LOG Lets first see the way using XP_LogEvent:Here I have created one SP which will raise an error “Divide by zero error encountered.” as I tried to do “10 / 0”. CREATE PROCEDURE TestEventViewer EXEC xp_logevent 60000, @msg, informational END CATCH Lets Execute this SP: EXEC TestEventViewer This will write entry in Event Viewer. Now open Event Viewer. You can find Event Viewer at Control Panel –> Administrative Tools –> Event Viewer. You will get en entry of Error there. So we can do this by Extended Stored Procedure: “xp_logevent”. Let see the parameters of this Procedure. First Parameter: “60000” is the Error Number Second Parameter: “@msg” is the message to be displayed in Event Viewer. Third Parameter: “informational” is the Error Level. It could be “informational”, “Error”, “Warning”. Now, Lets see by another way By Raiserror WITH LOG: It is the same way as we used Raiserror to Raise an Error. CREATE PROCEDURE TestEventViewer RAISERROR(@msg, 11, 1) WITH LOG END CATCH Lets Execute this SP: EXEC TestEventViewer. So By these ways we can make an entry to Event Viewer. Let me know if it helps you in any way |
 18+ years of Hands-on Experience
MICROSOFT CERTIFIED PROFESSIONAL (Microsoft SQL Server)
Proficient in .NET C#
Hands on working experience on MS SQL, DBA, Performance Tuning, Power BI, SSIS, and SSRS
18+ years of Hands-on Experience
MICROSOFT CERTIFIED PROFESSIONAL (Microsoft SQL Server)
Proficient in .NET C#
Hands on working experience on MS SQL, DBA, Performance Tuning, Power BI, SSIS, and SSRS